Delving into the intricacies of molecular biology, we present the DNA and Replication Worksheet Answer Key, an indispensable resource for students and educators alike. This comprehensive guide unravels the fundamental principles of DNA structure and replication, empowering readers with a deeper understanding of the genetic blueprint that governs all living organisms.
Through a meticulous exploration of DNA’s double helix architecture, nitrogenous bases, and sugar-phosphate backbone, this worksheet unravels the intricacies of genetic material. The detailed walkthrough of DNA replication, encompassing the pivotal roles of helicase, DNA polymerase, and ligase, provides a clear understanding of the mechanisms that ensure the faithful transmission of genetic information.
DNA Structure and Replication

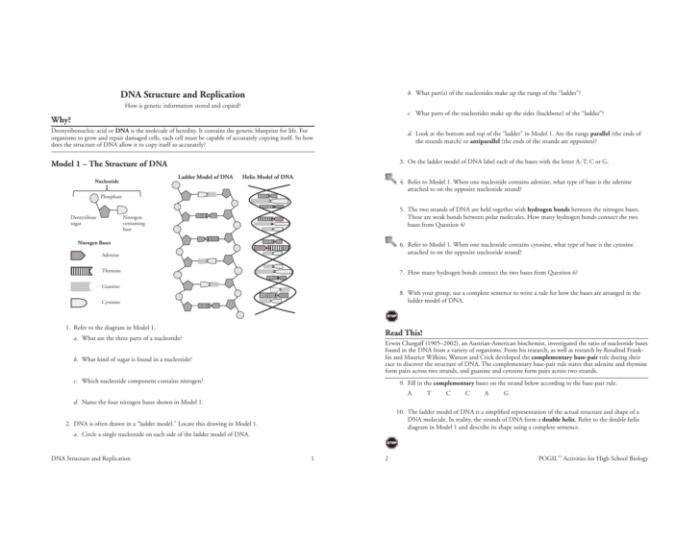
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a double helix molecule that contains the genetic instructions for all living organisms. It is composed of two strands of nucleotides, each of which consists of a sugar-phosphate backbone and a nitrogenous base. The nitrogenous bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C).
These bases pair up in a specific way: A with T, and G with C. This pairing is known as complementary base pairing.
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes a copy of its DNA. This process is essential for cell division, as each new cell needs its own copy of the DNA. DNA replication begins when the DNA double helix unwinds and the two strands separate.
Each strand then serves as a template for the synthesis of a new strand. The enzyme DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the new strands, following the complementary base pairing rules. Once the new strands are complete, they wind around each other to form a new double helix.
DNA Replication Worksheet
A DNA replication worksheet can be used to help students learn about the process of DNA replication. The worksheet typically includes a diagram%20of%20the%20DNA%20double%20helix, as well as a table that shows the complementary base pairing rules.
Students can use the worksheet to practice identifying the nitrogenous bases and to complete the replication process.
Here is a sample DNA replication worksheet with answer key:
- DNA Replication Worksheet
- Instructions:Complete the following DNA replication worksheet.
- Diagram of the DNA double helix:
- Table of complementary base pairing rules:
-
Nitrogenous Base Complementary Base Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Thymine (T) Adenine (A) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Cytosine (C) Guanine (G) - Replication steps:
- 1. The DNA double helix unwinds and the two strands separate.
- 2. Each strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new strand.
- 3. DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the new strands, following the complementary base pairing rules.
- 4. Once the new strands are complete, they wind around each other to form a new double helix.
- Answer key:
- The answer key will vary depending on the specific DNA sequence that is being replicated.
Types of DNA Replication
There are three main types of DNA replication:
- Semiconservative replication:This is the most common type of DNA replication. In semiconservative replication, each new DNA molecule consists of one original strand and one new strand.
- Conservative replication:In conservative replication, the original DNA double helix is not unwound. Instead, a new double helix is synthesized alongside the original double helix. The original double helix then serves as a template for the synthesis of a second new double helix.
- Dispersive replication:In dispersive replication, the original DNA double helix is unwound and the two strands are randomly distributed between the two new DNA molecules.
Errors in DNA Replication
Errors in DNA replication can occur for a variety of reasons, including exposure to radiation, chemicals, and errors by DNA polymerase. These errors can lead to mutations, which are changes in the DNA sequence. Mutations can be harmful, beneficial, or neutral.
Some mutations can cause genetic diseases, such as sickle cell anemia and cystic fibrosis.
DNA repair mechanisms help to correct errors in DNA replication. These mechanisms include:
- Base excision repair:This mechanism removes damaged bases from DNA.
- Nucleotide excision repair:This mechanism removes damaged nucleotides from DNA.
- Mismatch repair:This mechanism corrects errors in DNA replication.
Applications of DNA Replication
DNA replication is used in a variety of applications, including:
- Biotechnology:DNA replication is used to produce recombinant DNA, which is DNA that contains genes from two different organisms. Recombinant DNA can be used to create genetically modified organisms (GMOs).
- Forensics:DNA replication is used to amplify DNA samples for DNA fingerprinting. DNA fingerprinting is used to identify individuals and to determine paternity.
- Medicine:DNA replication is used to diagnose genetic diseases and to develop new treatments for genetic diseases.
Top FAQs: Dna And Replication Worksheet Answer Key
What is the significance of DNA replication?
DNA replication is crucial for cell division and the transmission of genetic information to daughter cells. It ensures the accurate duplication of genetic material, preserving the integrity of genetic information across generations.
How does DNA polymerase contribute to DNA replication?
DNA polymerase is a key enzyme responsible for synthesizing new DNA strands. It reads the template strand and adds complementary nucleotides, ensuring the faithful duplication of genetic information.