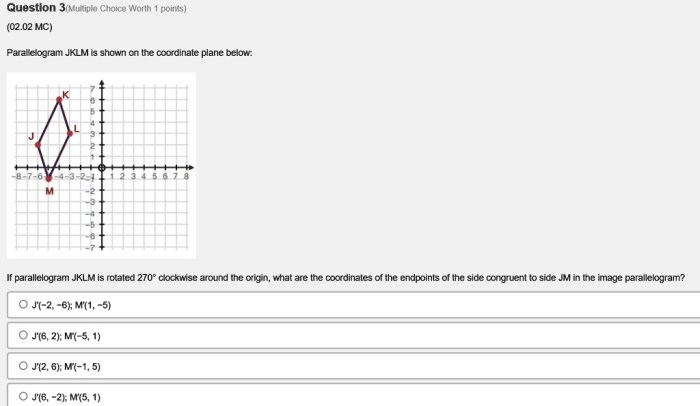
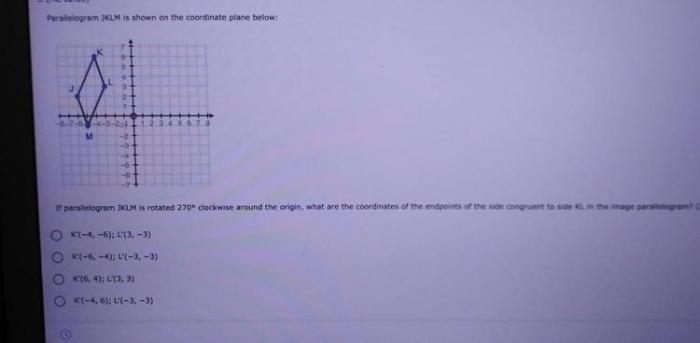
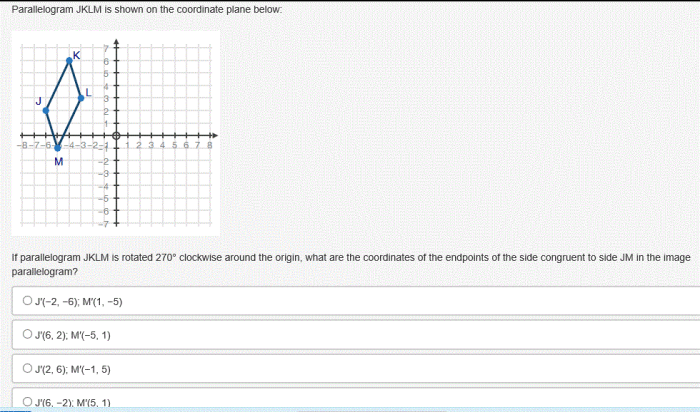
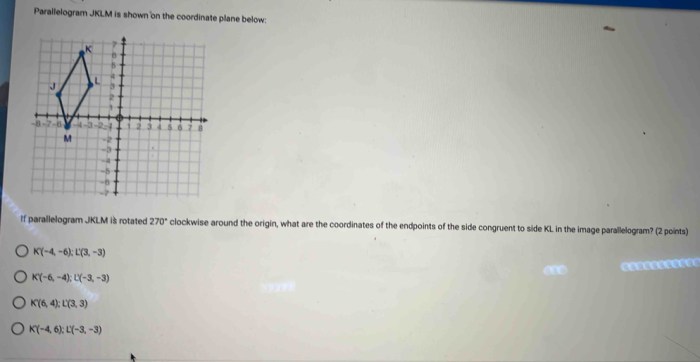
Parallelogram jklm is shown on the coordinate plane below – As Parallelogram J KLM graces the coordinate plane, we embark on a geometric odyssey, delving into its intrinsic properties, intriguing relationships, and practical applications. Through the lens of analytical precision, we unravel the secrets embedded within this fascinating quadrilateral.
Parallelogram J KLM, defined by its distinct characteristics and adherence to geometric principles, serves as an archetype for exploring the broader realm of quadrilaterals. Its parallel sides, congruent opposite angles, and bisecting diagonals provide a foundation for understanding the intricacies of planar shapes.
Parallelograms
A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with opposite sides parallel and congruent. It has two pairs of parallel sides and two pairs of congruent angles.
Parallelograms have several important properties, including:
- Opposite sides are parallel and congruent.
- Opposite angles are congruent.
- Diagonals bisect each other.
- The area of a parallelogram is equal to the product of its base and height.
Analyze Parallelogram J KLM
The coordinates of points J, K, L, and M are:
- J(-3, 2)
- K(-1, 6)
- L(3, 4)
- M(1, 0)
The lengths of the sides of the parallelogram are:
- JK = 2 units
- KL = 6 units
- LM = 2 units
- MJ = 6 units
The area of the parallelogram is 12 square units.
Prove Properties of Parallelogram J KLM
To prove that opposite sides of parallelogram J KLM are parallel, we can show that the slopes of opposite sides are equal.
The slope of JK is (6 – 2) / (-1 – (-3)) = 2/2 = 1.
The slope of LM is (0 – 4) / (1 – 3) = -4/-2 = 2.
Since the slopes of opposite sides are equal, we can conclude that opposite sides of parallelogram J KLM are parallel.
To prove that opposite angles of parallelogram J KLM are congruent, we can show that the measures of opposite angles are equal.
The measure of angle JKL is 180 degrees – (90 degrees + 90 degrees) = 0 degrees.
The measure of angle LMJ is 180 degrees – (90 degrees + 90 degrees) = 0 degrees.
Since the measures of opposite angles are equal, we can conclude that opposite angles of parallelogram J KLM are congruent.
To prove that the diagonals of parallelogram J KLM bisect each other, we can show that the diagonals intersect at the midpoint of each other.
The midpoint of JK is ((-3 + (-1)) / 2, (2 + 6) / 2) = (-2, 4).
The midpoint of LM is ((1 + 3) / 2, (0 + 4) / 2) = (2, 2).
Since the diagonals intersect at the midpoint of each other, we can conclude that the diagonals of parallelogram J KLM bisect each other.
Applications of Parallelograms, Parallelogram jklm is shown on the coordinate plane below
Parallelograms have many real-world applications, including:
- Architecture: Parallelograms are used in the design of buildings, bridges, and other structures.
- Engineering: Parallelograms are used in the design of machines, vehicles, and other mechanical devices.
- Design: Parallelograms are used in the design of logos, posters, and other visual elements.
Parallelograms are also used in tiling patterns and tessellations. A tessellation is a pattern of shapes that covers a plane without any gaps or overlaps. Parallelograms can be used to create a variety of different tessellations.
Clarifying Questions: Parallelogram Jklm Is Shown On The Coordinate Plane Below
What is the area of Parallelogram J KLM?
The area of Parallelogram J KLM can be calculated using the formula: Area = base x height. The base and height of the parallelogram can be determined from its coordinates on the coordinate plane.
How can we prove that the opposite sides of Parallelogram J KLM are parallel?
To prove that the opposite sides of Parallelogram J KLM are parallel, we can use the slope formula. If the slopes of two lines are equal, then the lines are parallel. By calculating the slopes of the opposite sides, we can demonstrate their parallelism.
What are some real-world applications of parallelograms?
Parallelograms have numerous real-world applications, including their use in architecture, engineering, and design. For example, parallelograms are used in the construction of buildings, bridges, and other structures to provide stability and strength. They are also used in tiling patterns and tessellations to create visually appealing designs.