Unit 1 exploring one variable statistics answer key – Embark on a statistical odyssey with Unit 1 Exploring One Variable Statistics, your comprehensive guide to deciphering the language of data. Delve into the fascinating realm of central tendency and dispersion, unraveling the mysteries of the normal distribution and sampling distributions.
Prepare to master hypothesis testing and confidence intervals, empowering you to make informed decisions based on data.
As we navigate this statistical landscape, we will uncover the nuances of each concept, exploring its advantages and limitations. Through engaging examples and insightful explanations, you will gain a profound understanding of one-variable statistics, enabling you to confidently analyze and interpret data in any field.
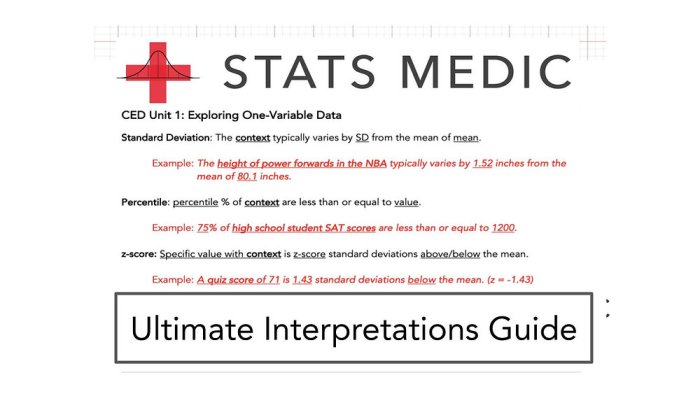
1. Introduction
One-variable statistics is a branch of statistics that deals with the analysis of data that consists of a single variable. It is used to describe the central tendency and dispersion of a data set, and to make inferences about the population from which the data was drawn.
Examples of one-variable statistics include the mean, median, mode, range, variance, and standard deviation.
2. Measures of Central Tendency
Mean
The mean is the arithmetic average of a set of data. It is calculated by adding up all the values in the data set and dividing by the number of values.
Median
The median is the middle value in a data set when assorted in ascending order. If there are two middle values, the median is the average of the two middle values.
Mode, Unit 1 exploring one variable statistics answer key
The mode is the value that occurs most frequently in a data set. A data set can have more than one mode.
3. Measures of Dispersion
Range
The range is the difference between the largest and smallest values in a data set.
Variance
The variance is a measure of how spread out a data set is. It is calculated by finding the average of the squared differences between each value in the data set and the mean.
Standard Deviation
The standard deviation is the square root of the variance. It is a measure of how much the values in a data set deviate from the mean.
4. Normal Distribution
The normal distribution is a bell-shaped distribution that is often used to model real-world data. It is characterized by its mean, median, and standard deviation.
The properties of the normal distribution include:
- The mean, median, and mode are all equal.
- The distribution is symmetric around the mean.
- The area under the curve is 1.
5. Sampling Distributions
A sampling distribution is a probability distribution of a statistic that is calculated from a sample of data. The Central Limit Theorem states that the sampling distribution of the mean will be approximately normal, regardless of the shape of the population distribution.
6. Hypothesis Testing: Unit 1 Exploring One Variable Statistics Answer Key

Hypothesis testing is a statistical procedure that is used to determine whether there is a significant difference between two or more groups.
The steps involved in hypothesis testing are:
- State the null and alternative hypotheses.
- Collect data.
- Calculate the test statistic.
- Determine the p-value.
- Make a decision.
7. Confidence Intervals
A confidence interval is a range of values that is likely to contain the true value of a population parameter.
The steps involved in constructing a confidence interval are:
- Calculate the sample mean and standard deviation.
- Find the critical value.
- Calculate the margin of error.
- Construct the confidence interval.
Common Queries
What is the difference between mean, median, and mode?
Mean is the average of all values in a dataset, median is the middle value, and mode is the most frequently occurring value.
How do I calculate the standard deviation?
Standard deviation is the square root of the variance, which is the average of the squared differences between each value and the mean.
What is the Central Limit Theorem?
The Central Limit Theorem states that the sampling distribution of means will be approximately normal, regardless of the shape of the population distribution.