Geometry mid year test study guide topic 1 geometry basics – Dive into Geometry Mid Year Test Study Guide Topic 1: Geometry Basics, an essential guide that empowers you to conquer the fundamentals of geometry. Prepare for success as we explore points, lines, planes, angles, shapes, and more, unlocking a world of geometric knowledge.
With clear explanations, real-world examples, and engaging discussions, this study guide will ignite your understanding of geometry and equip you with the confidence to excel in your mid-year test.
Geometry Basics: Geometry Mid Year Test Study Guide Topic 1 Geometry Basics

Geometry is the branch of mathematics that deals with the properties of space and shapes. It is a fundamental subject that has applications in various fields, including architecture, engineering, design, and computer graphics.
The basic concepts of geometry include points, lines, planes, and angles. Points are dimensionless objects that represent locations in space. Lines are one-dimensional objects that extend infinitely in both directions. Planes are two-dimensional objects that extend infinitely in all directions.
Angles are formed by the intersection of two lines or planes.
There are many different types of geometric shapes, each with its own unique properties. Some of the most common shapes include triangles, quadrilaterals, circles, and spheres.
Angles and Their Measurement
Angles are measured in degrees, with a full circle measuring 360 degrees. There are three main types of angles: acute angles, obtuse angles, and right angles. Acute angles measure less than 90 degrees, obtuse angles measure more than 90 degrees, and right angles measure exactly 90 degrees.
Angles can be combined to form larger angles. Two angles that add up to 90 degrees are called complementary angles. Two angles that add up to 180 degrees are called supplementary angles.
Triangles
Triangles are three-sided polygons. They are classified by the length of their sides and the measure of their angles.
- Equilateral triangles have three equal sides and three equal angles.
- Isosceles triangles have two equal sides and two equal angles.
- Scalene triangles have no equal sides and no equal angles.
The Pythagorean theorem is a fundamental theorem in geometry that relates the lengths of the sides of a right triangle.
Quadrilaterals
Quadrilaterals are four-sided polygons. They are classified by the length of their sides and the measure of their angles.
- Squares have four equal sides and four right angles.
- Rectangles have four equal angles and opposite sides that are equal in length.
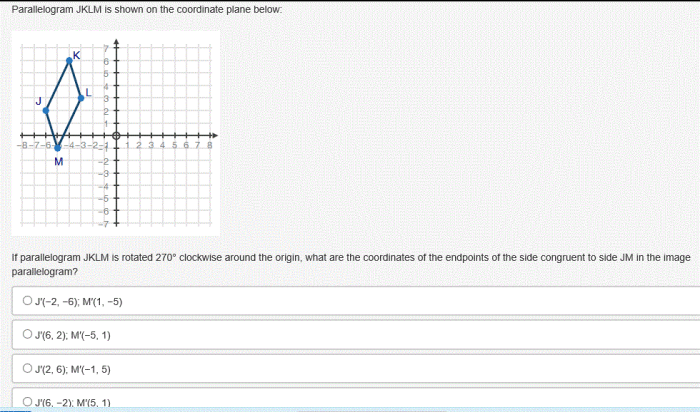
- Parallelograms have opposite sides that are parallel and equal in length.
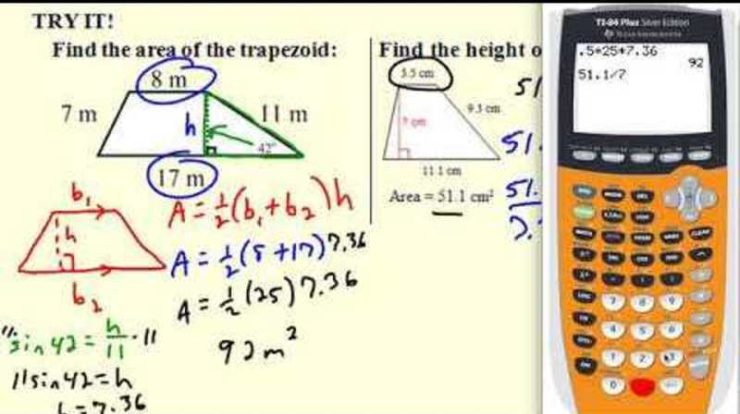
- Trapezoids have one pair of parallel sides.
Special quadrilaterals include kites and rhombuses.
Circles, Geometry mid year test study guide topic 1 geometry basics
Circles are two-dimensional shapes that are defined by a center point and a radius. The radius is the distance from the center point to any point on the circle.
The circumference of a circle is the distance around the circle. The area of a circle is the amount of space inside the circle.
Area and Volume
Area is a measure of the size of a two-dimensional surface. Volume is a measure of the size of a three-dimensional object.
The area of a triangle is calculated by multiplying the base by the height and dividing by 2. The area of a rectangle is calculated by multiplying the length by the width. The area of a circle is calculated by multiplying the radius squared by pi.
The volume of a cube is calculated by multiplying the length of one side by itself three times. The volume of a rectangular prism is calculated by multiplying the length by the width by the height.
Transformations
Transformations are operations that change the size, shape, or orientation of a geometric shape.
- Translations move a shape from one place to another without changing its size or shape.
- Rotations turn a shape around a fixed point.
- Reflections flip a shape over a line.
Transformations are used in geometry to create new shapes and to solve problems.
FAQ
What is the Pythagorean theorem?
The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
What is the difference between an acute and an obtuse angle?
An acute angle is less than 90 degrees, while an obtuse angle is greater than 90 degrees.
What is the formula for the area of a circle?
The formula for the area of a circle is A = πr², where r is the radius of the circle.