Embark on a journey into the realm of cellular biology with our comprehensive AP Biology Membrane Structure and Function Worksheet PDF. Delve into the intricate world of cell membranes, their composition, and their vital role in maintaining cellular homeostasis.
This worksheet unravels the mysteries of membrane structure, exploring the phospholipid bilayer, embedded proteins, and the diverse roles of membrane carbohydrates. Dive deeper into membrane function, understanding the mechanisms of passive and active transport, facilitated diffusion, and the crucial role of membranes in cell signaling.
Membrane Structure
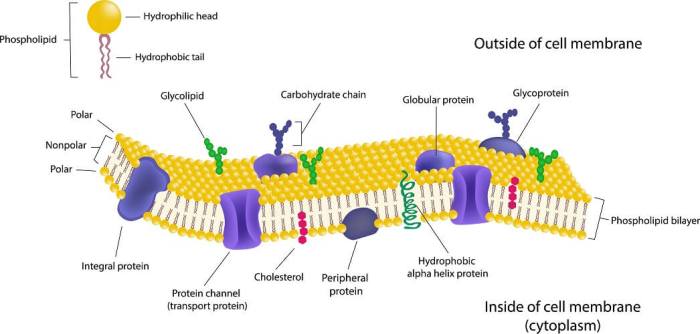
Cell membranes are complex structures that surround and protect cells. They regulate the passage of substances into and out of the cell, and they play a role in cell signaling. The structure of the cell membrane is essential for its function.The
cell membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer. Phospholipids are molecules that have a hydrophilic (water-loving) head and a hydrophobic (water-hating) tail. The hydrophilic heads face outward, where they interact with water, and the hydrophobic tails face inward, where they interact with each other.
This arrangement creates a barrier that prevents water-soluble molecules from passing through the membrane.Embedded in the phospholipid bilayer are proteins. These proteins can be classified into two types: integral proteins and peripheral proteins. Integral proteins span the entire membrane, from the extracellular side to the cytoplasmic side.
Peripheral proteins are attached to the surface of the membrane, either on the extracellular side or the cytoplasmic side.Carbohydrates are also attached to the cell membrane. These carbohydrates are attached to the proteins and lipids of the membrane, and they form a glycocalyx.
The glycocalyx protects the cell from damage and helps the cell to adhere to other cells.
Membrane Function
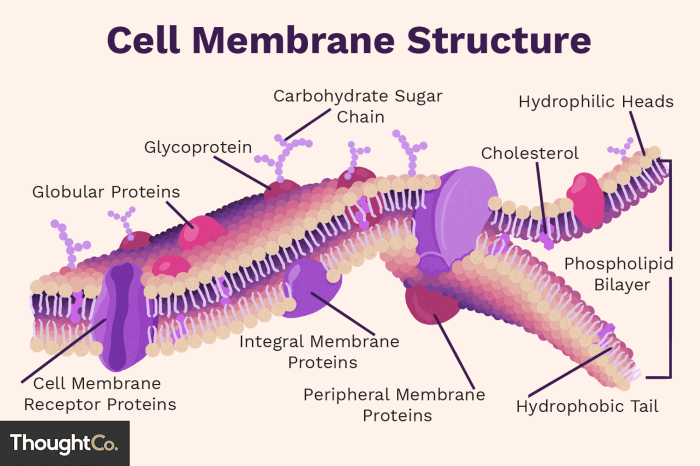
The cell membrane regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell. This process is essential for the cell’s survival. The cell membrane allows nutrients to enter the cell and waste products to leave the cell. It also prevents harmful substances from entering the cell.There
are three main mechanisms of membrane transport: passive diffusion, active transport, and facilitated diffusion. Passive diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. This process does not require energy. Active transport is the movement of molecules from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration.
This process requires energy. Facilitated diffusion is the movement of molecules across a membrane with the help of a carrier protein. This process does not require energy.The cell membrane also plays a role in cell signaling. Cell signaling is the process by which cells communicate with each other.
The cell membrane contains receptors that bind to signaling molecules. When a signaling molecule binds to a receptor, it triggers a cascade of events that leads to a change in the cell’s behavior.
Membrane Dynamics
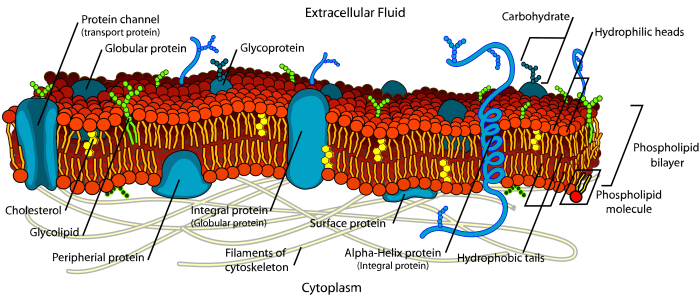
The cell membrane is not a static structure. It is constantly changing shape and composition. This process is known as membrane fluidity. Membrane fluidity is essential for the cell’s survival. It allows the cell to respond to changes in its environment and to repair itself when it is damaged.The
cytoskeleton is a network of proteins that helps to maintain the shape and function of the cell membrane. The cytoskeleton is composed of three types of proteins: microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules. Microfilaments are the smallest of the three types of cytoskeletal proteins.
They are composed of the protein actin. Intermediate filaments are larger than microfilaments. They are composed of a variety of proteins. Microtubules are the largest of the three types of cytoskeletal proteins. They are composed of the protein tubulin.The
cytoskeleton helps to maintain the shape of the cell membrane by providing a framework that the membrane can attach to. The cytoskeleton also helps to regulate membrane fluidity by controlling the movement of proteins and lipids within the membrane.
Membrane Disorders: Ap Biology Membrane Structure And Function Worksheet Pdf
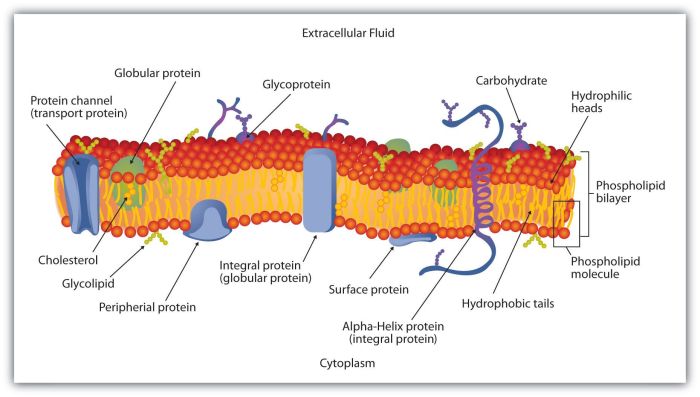
Membrane disorders are a group of diseases that affect the structure and function of the cell membrane. Membrane disorders can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetic defects, environmental toxins, and infections.There are a number of different types of membrane disorders.
Some of the most common types include:
Lipid storage diseases
These diseases are caused by a deficiency of enzymes that are responsible for breaking down lipids. This can lead to a buildup of lipids in the cell membrane, which can interfere with the membrane’s function.
Membrane transport disorders
These diseases are caused by a deficiency of proteins that are responsible for transporting molecules across the cell membrane. This can lead to a buildup of molecules in the cell or a depletion of molecules in the cell.
Signal transduction disorders
These diseases are caused by a deficiency of receptors that are responsible for binding to signaling molecules. This can interfere with the cell’s ability to respond to signals from other cells.Membrane disorders can have a wide range of symptoms, depending on the type of disorder.
Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Muscle pain
- Cramps
- Numbness
- Tingling
- Vision problems
- Hearing problems
- Cognitive problems
- Behavioral problems
Membrane disorders can be treated with a variety of medications, depending on the type of disorder. Some of the most common types of medications include:
Enzyme replacement therapy
This therapy is used to treat lipid storage diseases. It involves replacing the missing enzyme with a healthy enzyme.
Membrane transport inhibitors
These medications are used to treat membrane transport disorders. They block the transport of molecules across the cell membrane, which can help to restore the balance of molecules in the cell.
Signal transduction inhibitors
These medications are used to treat signal transduction disorders. They block the binding of signaling molecules to receptors, which can help to prevent the cell from responding to signals from other cells.
General Inquiries
What is the primary function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell, maintaining cellular homeostasis.
Explain the role of membrane proteins in membrane function.
Membrane proteins facilitate the transport of molecules across the membrane, act as receptors for signaling molecules, and participate in cell adhesion and recognition.
How does membrane fluidity affect membrane function?
Membrane fluidity allows for membrane flexibility and dynamic changes in shape, enabling processes such as cell movement and membrane fusion.