Dive into the US Bodies of Water Quiz, where we explore the vast and diverse waterways that shape our nation. From the Atlantic’s salty embrace to the Mississippi’s mighty flow, each body of water holds a unique story.
This quiz will test your knowledge of the United States’ most iconic rivers, lakes, and oceans, as well as their ecological and economic significance. So, ready your paddles and let’s embark on a watery adventure!
U.S. Bodies of Water Geography

The United States is home to a diverse range of water bodies, including oceans, lakes, rivers, and gulfs. These bodies of water play a crucial role in the country’s economy, transportation, and recreation.
The following map illustrates the major U.S. bodies of water, organized by region:
- East Coast:Atlantic Ocean, Gulf of Maine, Chesapeake Bay
- West Coast:Pacific Ocean, Gulf of California, Puget Sound
- Midwest:Great Lakes (Lake Superior, Lake Michigan, Lake Huron, Lake Erie, Lake Ontario), Mississippi River
Notable U.S. Water Bodies
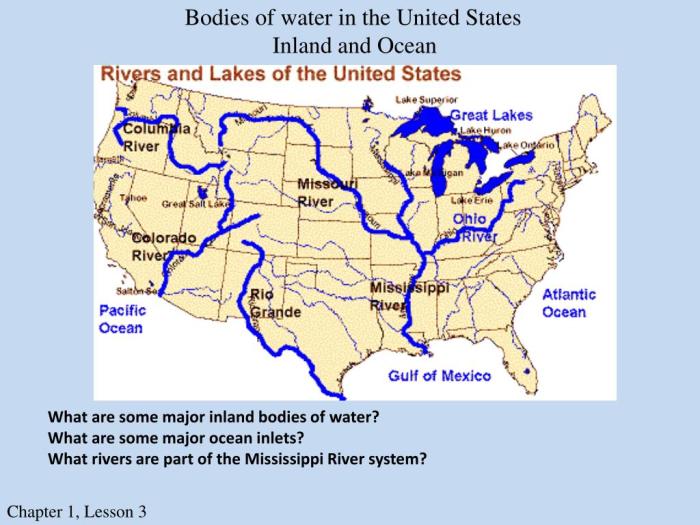
The United States is blessed with a diverse array of water bodies, from towering mountain lakes to mighty rivers that have shaped the nation’s history and economy.
Lake Superior
Nestled along the U.S.-Canada border, Lake Superior is the largest freshwater lake in the world by surface area. This colossal body of water spans over 31,700 square miles, stretching 350 miles in length and 160 miles in width. With an average depth of 483 feet and a maximum depth of 1,333 feet, Lake Superior holds a staggering 10% of the world’s surface freshwater.
For those interested in expanding their knowledge of bodies of water, an online quiz is a great starting point. As a curious explorer, you may find yourself venturing beyond the quiz and discovering fascinating tales like that of “the blind seer of Ambon,” a legendary figure who navigated the seas despite his visual impairment.
Such stories remind us of the remarkable diversity and captivating narratives associated with our planet’s bodies of water.
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the lifeblood of the United States, stretching 2,350 miles from its source at Lake Itasca in Minnesota to its delta at the Gulf of Mexico. This iconic waterway has played a pivotal role in the nation’s history, serving as a vital transportation route and a source of sustenance for centuries.
Great Salt Lake
Located in the western United States, the Great Salt Lake is a unique and fascinating body of water. With a salinity eight times that of the ocean, it is one of the saltiest lakes in the world. This extreme salinity supports a unique ecosystem, including brine shrimp and alkali flies, that have adapted to the harsh conditions.
Ecological Importance of U.S. Bodies of Water
U.S. bodies of water, including rivers, lakes, oceans, and wetlands, play a crucial role in supporting a diverse array of ecosystems and wildlife habitats. These aquatic environments provide essential resources for a vast number of species, including fish, birds, mammals, and plants.
Wetlands
Wetlands, transitional areas between land and water, are particularly important for their ecological functions. They act as natural filters, removing pollutants and excess nutrients from water. Additionally, wetlands serve as flood control systems, absorbing excess water during heavy rainfall and releasing it gradually, reducing the risk of flooding downstream.
Moreover, wetlands provide diverse habitats for a wide range of species, including waterfowl, amphibians, reptiles, and fish.
Endangered Species
Many endangered or threatened species in the United States rely on specific bodies of water for their survival. For example, the California condor depends on the coastal mountains of California for nesting and foraging, while the Florida manatee relies on warm-water estuaries and rivers for shelter and feeding.
Economic Significance of U.S. Bodies of Water: Us Bodies Of Water Quiz
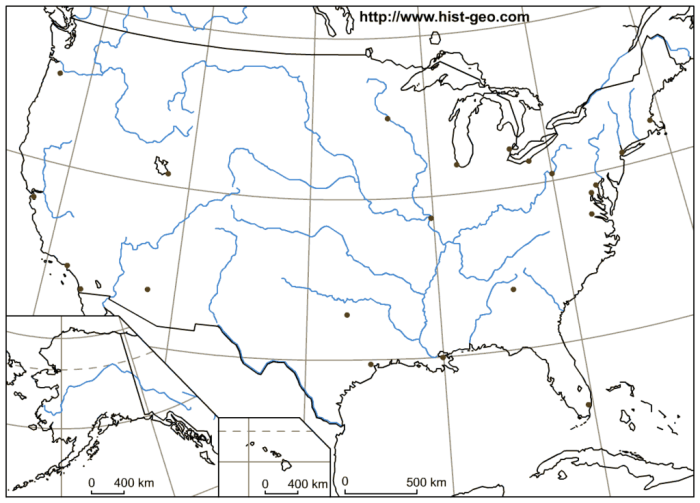
The vast network of rivers, lakes, and oceans surrounding the United States has played a pivotal role in shaping the nation’s economic prosperity. These water bodies have served as vital arteries for transportation, trade, and tourism, fostering economic growth and connectivity.
Transportation and Trade
The Mississippi River system, spanning over 2,300 miles, has been a primary waterway for transporting goods and people since the 18th century. It connects the Great Lakes region to the Gulf of Mexico, facilitating the movement of agricultural products, industrial materials, and consumer goods.
Similarly, the Great Lakes, with their vast network of canals and locks, have enabled the transportation of iron ore, coal, and grain between the Midwest and the East Coast.Coastal cities such as New York, Los Angeles, and Seattle have developed into major international ports, handling a significant portion of the nation’s foreign trade.
The Port of New York and New Jersey alone accounts for over 25% of the value of all U.S. waterborne imports and exports.
Tourism
The scenic beauty and recreational opportunities offered by U.S. water bodies attract millions of tourists each year. Coastal areas, such as Florida’s beaches and California’s coastline, are renowned for their surfing, swimming, and sunbathing. Inland lakes and rivers provide ample opportunities for fishing, boating, and other water-based activities.
National parks and monuments, such as the Grand Canyon and Yosemite National Park, showcase stunning water features that draw visitors from around the world.
Hydroelectric Power and Industries
Water bodies have been instrumental in generating hydroelectric power, a renewable energy source that accounts for over 6% of U.S. electricity production. Dams constructed on rivers harness the power of flowing water to generate electricity, providing a clean and sustainable source of energy.Water
is also essential for supporting industries such as fishing and agriculture. The oceans and inland waterways provide a vast source of seafood, including fish, shellfish, and crustaceans. Agriculture relies heavily on water for irrigation, enabling the production of crops that feed the nation and the world.
Economic Impact
Water-related activities contribute significantly to the U.S. economy. The tourism industry alone generates over $1.2 trillion annually and supports millions of jobs. The transportation and trade sectors that utilize water bodies contribute billions of dollars to the GDP. Additionally, the fishing and agricultural industries provide food and raw materials, supporting local economies and contributing to the nation’s food security.In
conclusion, U.S. bodies of water have played a multifaceted role in the nation’s economic development. They have served as vital transportation routes, facilitated international trade, attracted tourists, generated hydroelectric power, and supported key industries. The economic significance of these water bodies is undeniable, contributing to the prosperity and well-being of the United States.
Environmental Challenges Facing U.S. Bodies of Water
U.S. bodies of water face a multitude of environmental challenges that threaten their health and ecological balance. These challenges include pollution, climate change, and invasive species, each posing unique risks and consequences.
Water pollution is a significant issue affecting U.S. bodies of water. Pollutants from various sources, including industrial wastewater, agricultural runoff, and sewage, contaminate water sources, degrading water quality and harming aquatic life.
Sources and Consequences of Water Pollution
- Industrial Wastewater:Industrial processes generate toxic chemicals and heavy metals that are often discharged into water bodies, contaminating them and posing health risks to humans and wildlife.
- Agricultural Runoff:Fertilizers and pesticides used in agriculture can leach into waterways, causing nutrient pollution and algal blooms, which deplete oxygen levels and harm aquatic ecosystems.
- Sewage:Untreated or improperly treated sewage releases harmful bacteria and pathogens into water bodies, posing health risks and contributing to waterborne diseases.
Climate change also significantly impacts U.S. bodies of water. Rising temperatures are causing water levels to fluctuate, with some areas experiencing droughts while others face increased flooding. Additionally, warming waters affect aquatic ecosystems, altering species distribution and disrupting food chains.
Impacts of Climate Change on Water Bodies
- Water Level Fluctuations:Changes in precipitation patterns due to climate change lead to extreme events such as droughts and floods, affecting water availability and ecosystem health.
- Warming Waters:Rising temperatures alter water chemistry and oxygen levels, affecting the distribution and survival of aquatic species.
- Ecosystem Disruptions:Climate change disrupts food chains and alters species interactions within aquatic ecosystems, leading to changes in biodiversity and ecological balance.
Conservation and Management of U.S. Bodies of Water
Protecting and sustainably managing U.S. bodies of water is crucial for preserving ecosystems, ensuring water security, and safeguarding human health. This involves efforts to protect water quality, restore habitats, and manage water resources effectively.
Government Agencies and Organizations
Various government agencies and organizations play significant roles in the conservation and management of U.S. bodies of water:
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA):Sets and enforces water quality standards, regulates pollution discharges, and provides funding for water quality protection programs.
- U.S. Army Corps of Engineers:Constructs and maintains dams, levees, and other water infrastructure, and manages navigable waterways.
- U.S. Geological Survey (USGS):Monitors water quality, streamflow, and groundwater levels, and conducts research on water resources.
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA):Manages coastal and marine ecosystems, monitors ocean health, and conducts research on climate change impacts.
Strategies for Protecting and Restoring Water Bodies, Us bodies of water quiz
Numerous strategies are employed to protect and restore water bodies, including:
- Water Quality Protection:Implementing pollution control measures, such as reducing agricultural runoff, controlling industrial discharges, and managing stormwater.
- Habitat Restoration:Restoring riparian zones, wetlands, and other aquatic habitats to improve water quality and support biodiversity.
- Water Management:Implementing water allocation plans, managing dams and reservoirs, and mitigating flood risks.
li> Water Conservation:Promoting water-efficient practices, such as low-flow appliances, rainwater harvesting, and drought-tolerant landscaping.
Successful Conservation Initiatives
Examples of successful conservation initiatives include:
- Chesapeake Bay Program:A multi-state partnership that has significantly reduced pollution and improved water quality in the Chesapeake Bay.
- Everglades Restoration Project:A massive undertaking to restore the natural flow of water through the Everglades ecosystem.
- Great Lakes Restoration Initiative:A federal program to address pollution, invasive species, and habitat loss in the Great Lakes.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite progress, U.S. bodies of water face ongoing challenges, including pollution, climate change, and population growth. Addressing these challenges requires continued efforts in conservation, management, and public education.
Key Questions Answered
What is the largest lake in the US?
Lake Superior
What is the longest river in the US?
Mississippi River
What is the saltiest lake in the US?
Great Salt Lake